It can be a concerning discovery for any webmaster or content marketer when they’ve experienced a drop in organic traffic and there seems to be absolutely no rhyme or reason as to why. There’s no need to panic, because we’re taking you through a step-by-step guide on what actions to take once you’ve noticed a drop in organic traffic, so you’re able to climb back to the top of those dizzy organic heights once again.
Step 1 – Check Your Google Analytics Tracking Is Working
Sometimes it might not be a loss in traffic itself, but actually a reporting issue. This can be due to a problem with the Google Analytics tracking code, any changes made to your website code can potentially create problems for the tracking code, meaning reporting issues can occur.
Make sure it correctly installed your tracking code. Go to your Google Analytics and navigate to:
- Admin
- Tracking Info
- Tracking Code
Here you can view the status at the top of the page.
Another recommended tool would be to use the Chrome extension Tag Assistant (by Google). Once installed, you’ll see your tracking ID when the extension icon is clicked, provided the Analytics tracking is working correctly.
Step 2 – Check If A Manual Penalty Has Been Issued
The second step is to discover whether the website has received a manual penalty from Google. A manual penalty is when an actual person (most likely somebody from the Google Quality team) has reviewed your site and issued a penalty manually themselves. This can happen for of a number of reasons and it can either be issued across the website as a whole i.e site-wide, or partial i.e. affecting just some pages.
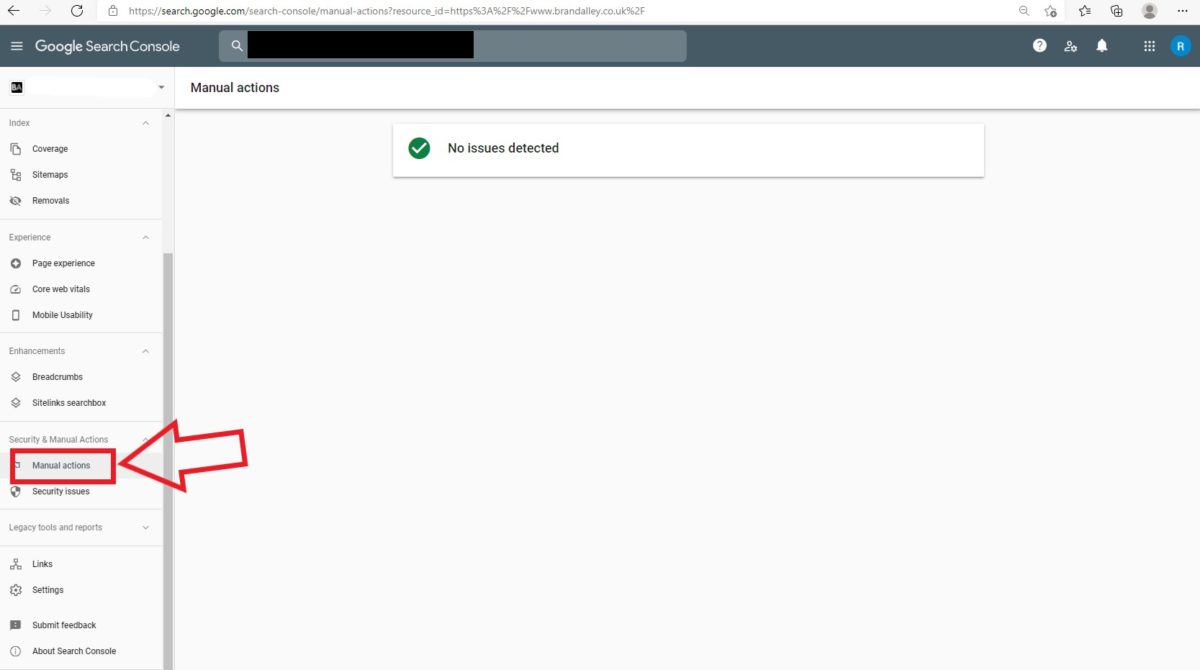
There are tools available to help you understand whether one has been issued. Start by checking your Google Search Console and navigate to:
- Security & Manual Actions
- Manual Actions
If there is no manual action issued, ‘no issues detected’ will be displayed.
If a manual penalty has been issued, whether partial or site-wide, then it will appear in this section of your Search Console. Read carefully as to why the penalty has been given and create a strategy to recover. Solve these reasons and then request Google to review the site again via Google Search Console.
Step 3 – Check If It’s Due To A Google Algorithm Update
Next we need to discover whether the website has dropped due to a Google algorithm update. If you receive a traffic drop from a Google update it doesn’t necessarily mean a penalty has been issued. With an algorithmic ‘penalty’ there is no manual checking from Google involved and because of this, a request for review can not be issued.
A loss of traffic following an algorithm update or algorithmic penalty is received for doing anything that would violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. Google uses clever filters to automatically detect if a website violates their guidelines. The most well-known and most common violations are around the Panda update (hitting sites that had low quality content) and the Penguin update (hitting sites who have manipulatively built links).
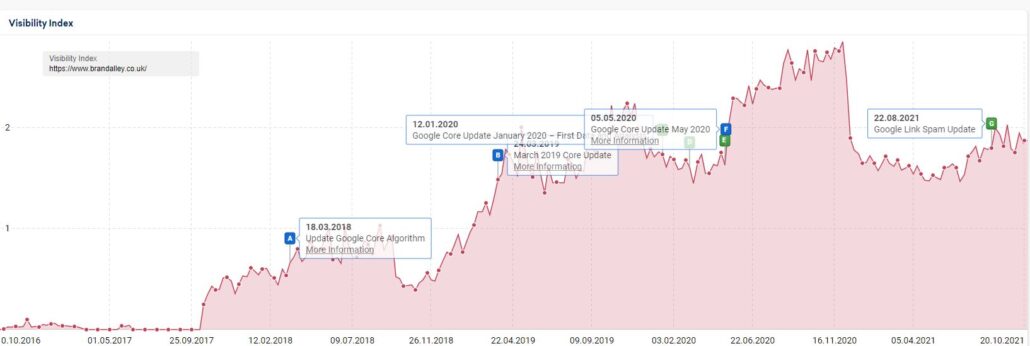
Sistrix is a great tool for understanding whether a website has been affected by a core algorithm update. See example below:
As you can see, the website above dropped following the September 2019 and January 2020 core algorithm updates but has started to recover following the Product Review Update in April 2021.
So if you think your website was hit by an algorithm update, find out what update could have caused this and start rectifying the reasons for it. The loss of traffic will be present until you’re able to clean up the issue and implement some solutions. Once a new core algorithm update is introduced, you should then be able to reap the benefits.
Step 4 – Complete A Site Audit
Consider if there were any changes made to the site when the loss in traffic occurred. Has there been a site migration that’s not been 301 redirected correctly? Were there any changes made to the site, like a redesign?
Either way, start completing a site audit to understand how search engines are crawling the site and gain insights into its overall SEO health. Things to look out for, for example, would be improving the site load time, fixing any indexing issues, checking your sitemap and robot.txt files, and making sure your 301 redirects are working properly.
SEMrush, Ahrefs and Sitebulb are some of our go-to tools we use to uncover any technical issues. They will help you break down the tasks to improve your website’s search engine visibility, or just feel free to contact us and we can take a look.
Step 5 – Check For Malware
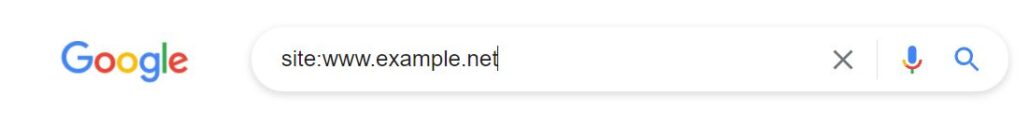
The next step is to complete a site command. To do this you need to enter into Google:
site: directly followed by your website URL. e.g.
site:https://wwwexample.com
This enables you to check your site for any malware. If you notice anything strange in Google’s results, like titles in your pages you haven’t created, then scan your website for malware. Take measures to ensure that your site no longer hosts malware, spam or any content the attacker may have installed.
Also check whether your website is on the Google safe browsing list by visiting the following URL (Make sure to replace the http://example.com/ with your actual URL.):
http://www.google.com/safebrowsing/diagnostic?site=http://example.com/
Google will put compromised websites into two categories:
Attack sites: Sites that host software that will infect visitor computers.
Compromised sites: Sites that have been hacked and host spam or other content that an attacker has installed.
In either case you will be told on the safebrowsing page above if your site falls into either of these categories.
Step 6 – Review Any Broken Or Lost Links
It’s also important to review whether there have been any sites linking to your website that are now either erroring or have been removed. When your site loses inbound links, it signals to search engines your site isn’t as authoritative anymore, which then leads to lower search rankings which in turn leads to a drop in organic traffic.
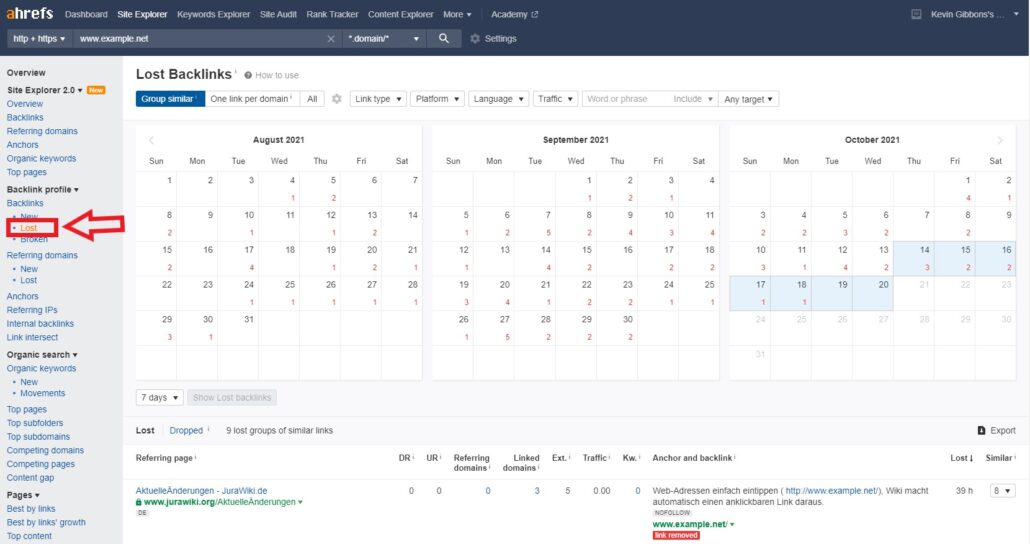
Tools such as Ahrefs will help you to identify any links that are broken or have been recently lost for any reason. Input your site’s URL into the lost backlinks tool (located under the backlink profile section) and it will automatically tell you the links that have been pointing to the site in the last 7 days but have now been removed. Adjust the dates to when the drop occurred and identify any links that were removed around this time. Then conduct outreach to these sites to try and reinstate these links.
Another reason could be due to broken links. The two most common reasons for broken backlinks to your website are:
- Your web team deletes or moves a page that has existing backlinks
- Or the site linking to you incorrectly inputs the URL when linking to you (e.g, they may accidentally add an unneeded character to the URL)
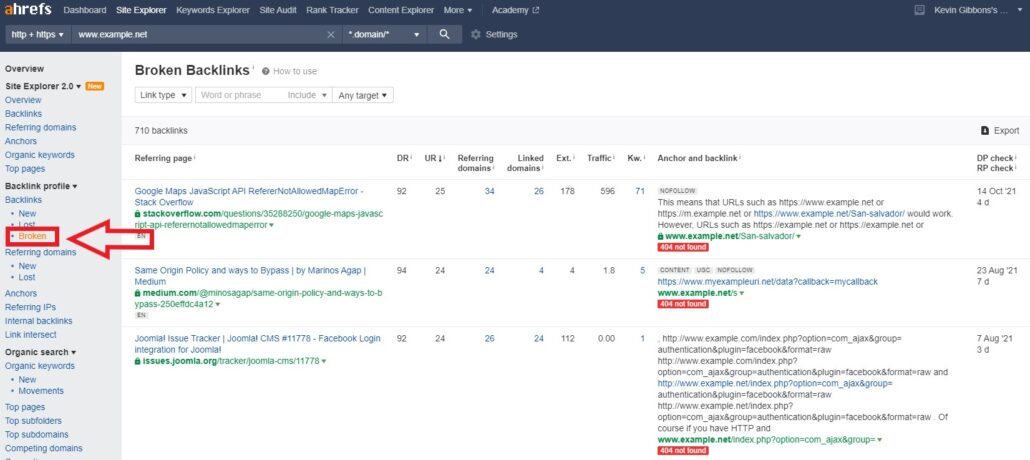
Again Ahrefs will provide you with a list of broken backlinks. Click on the ‘Broken’ link under the ‘Backlink Profile’ feature and input your site URL.
Again outreach to these websites to ask whether it’s possible to have the link reinstated.
Step 7 (a) – Review The Quality Of Your Content
In step 3 we discussed the Panda algorithm update that focused on reducing visibility for websites with poor quality content. Not only that, there has been research conducted that shows a correlation between longer content and higher rankings in search engine results. Therefore it’s really important to also assess the quality of your content and consider if there’s any outdated or irrelevant content.
What to really bear in mind when you’re looking for these pages is that you are looking for content that has little or no value to the visitor.
There are some great tools to use to identify the pages with low quality content:
Google Analytics
A great tool here to use is Google Analytics to assess the engagement levels of your pages and identify the pages with the highest bounce rate. Any with a high bounce rate might indicate a user is not accessing the information they’re looking for. Look at other user stats such as page views, amount of pages viewed and time on the page to determine a page’s overall performance.
Screaming Frog
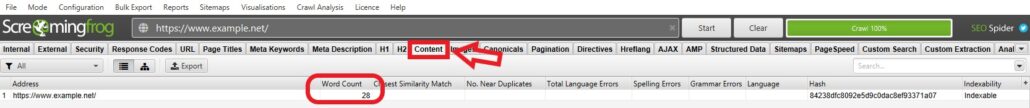
Another tool would be to use Screaming Frog which enables you to crawl the website and identify pages that have a particularly low word count by navigating to the content section.
Screaming Frog will allow you to sort by the lowest count first, so you can quickly identify pages that are light on content.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides you with the number of clicks, impressions, click-through-rate (CTR), and average position. So any pages listed that aren’t producing a high CTR should be analysed.
Through your analysis if you discover pages you think aren’t needed, analyse them to find out if there are any external links pointing to these pages. (Our friendly SEMrush and Ahrefs will help with this) and any pages that have external links pointing to them, you should no-index. For the pages with no backlinks, we recommend you remove these pages and 301 redirect them to an appropriate page.
Step 7 (b) – Review The Quality Of Your Content (Page Titles and Meta Descriptions)
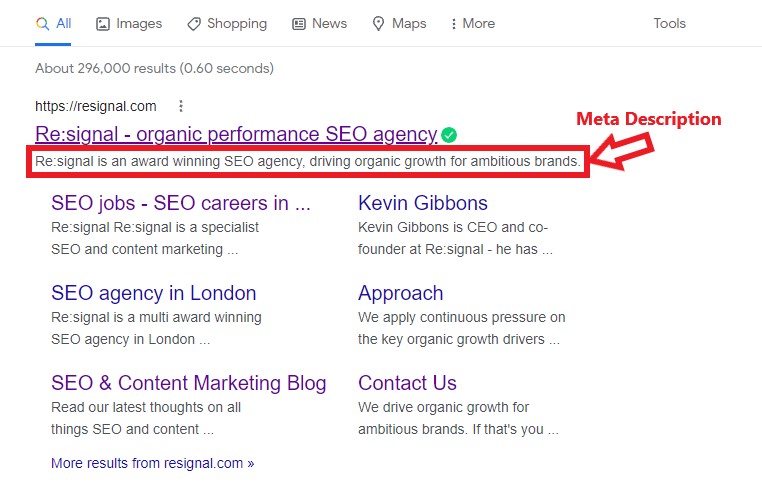
Another way to improve the quality of your content is to review your page titles (AKA HTML title tag) and meta descriptions.
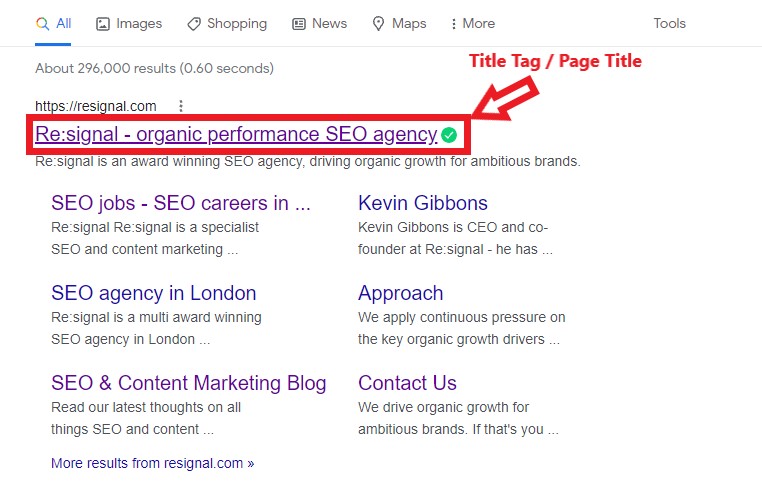
Your page titles are the blue clickable link you click on from search engine results and also the text that appears when hovering over a tab. The meta description is the text below the clickable link in search results that explains the content of the page.
Your page titles should make users want to click on it. They are an important ranking signal to search engines so they should ideally include your target phrase. Keep them within a 60 character limit and also ensure these are unique.
If you don’t set a meta description in your CMS, then search engines will lift a random couple of sentences from the page. This could potentially decrease the numbers of users that click through to your site. The need to all be unique and keep within a 155 character limit to avoid them truncating in results.
Step 8 – Complete a Competitor Analysis
A sudden drop in traffic might be a sign there are new players in the market, or old ones that have been focusing more heavily on SEO. So the next step would be to conduct a competitor analysis.
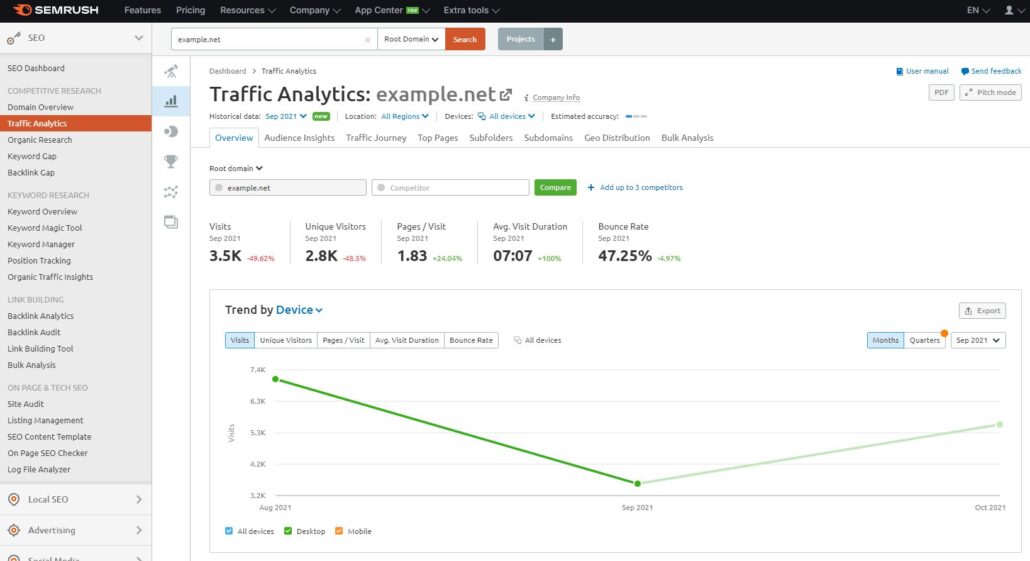
Completing a competitor SEO analysis can unearth some invaluable insights into potential opportunities and strategies and understand what is working and not working in your industry. The competitive research tools in SEMrush is a great starting point to see how your competitors are performing. The traffic analysis tool enables you to view estimated visits, top pages, and traffic, to mention just a few.
The backlink gap also allows you to compare your competitor’s backlink profile to your own. This way you can establish what sites are linking to your competitor’s site and not to your own, helping you to identify the sites to outreach to and collaborate with.
Summary
The most important thing to remember is to not panic. If you carry out these steps to identify the reasons why, you can then form a strategy to start to recover. Otherwise, the Re:signal team is always at hand to help, just contact us for more information.