A Complete Guide to Edge SEO: Everything You Wanted to Know
In the last few years, Edge computing has emerged as a type of cloud technology that sectors as diverse as civil engineering and video gaming have taken advantage of. It allows them to transfer data and carry out other types of changes on digital platforms much faster, without necessarily having the required manpower at hand.
And today, Edge computing is increasingly being used by SEOs as part of their range of tools to execute their campaigns – leading to the emergence of a strand of SEO referred to as Edge SEO. This blog aims to provide a complete guide to what Edge SEO is and how it can benefit you as an SEO professional.
In this blog you will learn:
- What is Edge computing?
- What are Content Delivery Networks?
- What is Edge SEO?
- What changes can you make with Edge SEO?
So without further ado, let’s first start by discussing what Edge computing actually is!
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a type of serverless cloud technology, used for processing and manipulating data. This form of cloud technology is used particularly to reduce latency – that is the speed at which it takes data to transfer from the cloud server to a user’s device. The Edge was primarily introduced as the demand for handling and storing data increased more and more amongst businesses. That said, this form of data processing was also purposed for other digital services, such as online video gaming, civil engineering and most importantly for SEOs, websites.
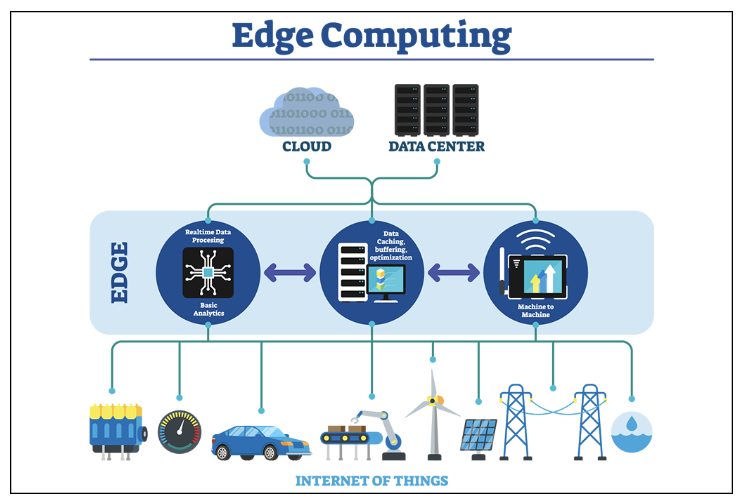
With Edge computing, all of your infrastructure is stored in the cloud, and accessed via a central data centre. However, what differentiates this cloud technology from others, is its use of connections to various other data centres located around the world – referred to as a content delivery network (CDN). It is this connection of various data centres, to one another, within a content delivery network, that reduces latency and increases both the speed and ease of transferring data.
What are Content Delivery Networks?
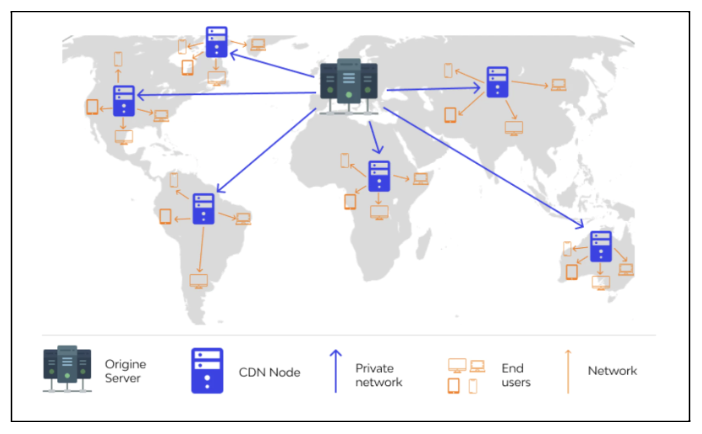
As mentioned above, Edge computing makes use of content delivery networks to transfer data. These CDNs are at the core of how the Edge operates. Each data centre placed in their local region is referred to as a node and since it is at the very end point of the network, or “edge”, that’s where the name of this computing technology comes from. Therefore, a CDN is also often referred to as an “Edge server”.
Due to the popularity of content delivery networks, many enterprise businesses, such as Facebook, Netflix, Amazon and IBM are leveraging this technology to serve their traffic.
How Does a Content Delivery Network Work?
To understand how a CDN works, let’s apply what we’ve discussed above in practical terms with a real world scenario. Let’s say we have a hypothetical sports apparel e-commerce website. Our online business uses a content delivery network to transfer data, and our central data centre is positioned in Toronto, Canada.
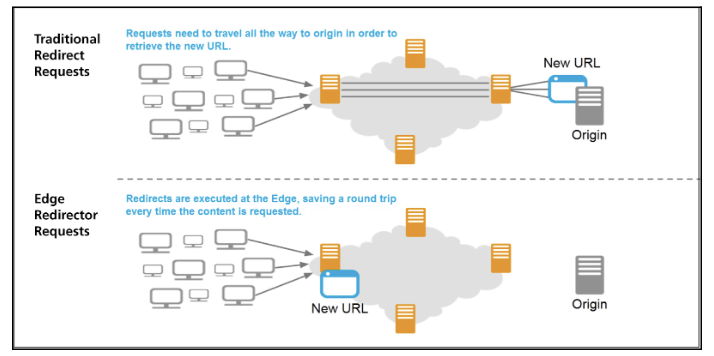
Also In our scenario, we have a user in New Delhi, India. Our user from New Delhi accesses the running shoes category page of our sports e-commerce site. What happens next is that our content delivery network provides the content from a cached, static copy of the page, stored in the regional data centre / Edge server located in Delhi, rather than the origin server in Toronto. The use of a cached version of the page from a local Edge server removes the need to access the contents of the page all the way from the origin server. Since the access request for the page content does not need to travel the distance required to Toronto, but rather only to the local node in Delhi, it allows for the contents of the page to be provided to the user, on his device at a much faster rate. This improves page speed, TTFB (time before the user can interact with the page itself), and the overall user experience too.
With businesses operating internationally, having data instantly ready for customers across various markets is an obvious benefit. Therefore, the benefits of a CDN speak for themselves.
However, the benefits of a CDN are not just limited to ease of data transfer. There are many other advantages that a CDN can provide. Here are just a few other benefits of content delivery networks:
- Increase in availability of content
- Website security
- Improvement in website load times
- Reduced bandwidth costs
To recap, we’ve now discussed what Edge computing is, what content delivery networks are, how they work as well as their benefits. But what are examples of CDNs and which ones are the best? We’ll discuss these two questions in the next section.
What are the Top CDNs Available Today?
There are four main CDNs that dominate the market at the moment.
- Akamai
One of the leading CDN platforms in the market, Akamai was founded back in 1998 and caters to businesses of varying sizes, including Best Buy, Honda, and The Washington Post.
With almost 275,000 servers in over 135 countries, Akamai has a far-reaching global scale. It can provide low latency, a range of security solutions, compatibility with various cloud environments as well as advanced analytics tracking.
- CloudFront (powered by Amazon)
Amazon CloudFront launched back in 2008 and is a content delivery network powered by Amazon Web Services.
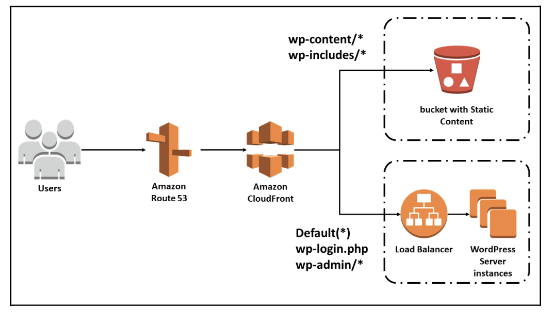
Since it is from Amazon, it takes advantage of AWS’ global infrastructure to provide content to users worldwide.
- Cloudflare
Cloudflare is one of the most popular content delivery networks on the market. The American service is both friendly to use for beginners and experts alike. Many brands and businesses use Cloudflare, such as IBM, L’Oréal, Shopfiy and Panasonic. Cloudflare also makes use of serverless workers to deploy SEO changes on the Edge – we’ll discuss this later in more detail.
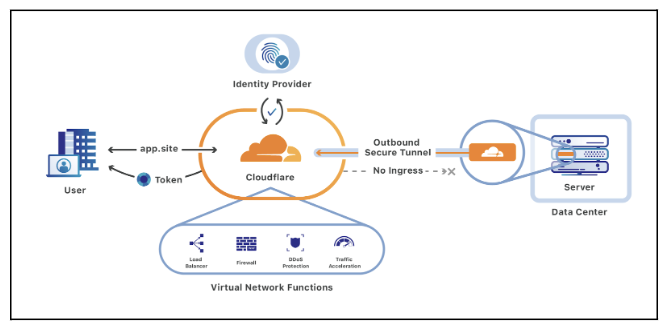
Cloudflare is easy to set up, and you can monitor performance from a single panel. You can also have access to more than 180 data centres around the world.
- Fastly
Fastly is focused on giving a platform specifically for web content and web app optimisation. Many online publications and digital media companies have taken advantage of Fastly’s capabilities, such as The New York Times and Reddit.
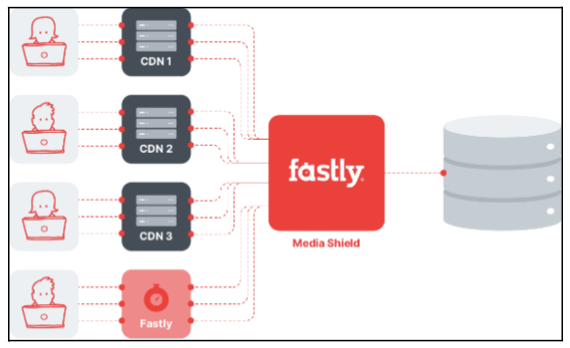
One of Fastly’s most useful capabilities is just how configurable the service is. For instance, there’s support for different types of video caching. There are also various controls if you want to manipulate HTTP headers, to configure how your content is served to the user.
What is Edge SEO?
As Edge technology continues to advance so do its capabilities. It is no longer just about transferring data. You can now carry out computation on the Edge. You can manipulate stored data on the Edge and also make changes to a web page before it is even served to the user, without interfering with the primary site on the origin server. In fact, the Edge is growing at such a vast rate that the types of changes you can make are becoming almost limitless.
This is where Edge SEO comes in. With the almost limitless capabilities the Edge offers for you to make changes to a site, SEOs can leverage Edge technology to assist in on-site implementation, testing, and research processes as part of their technical SEO and content strategies.
Besides updating pages, Edge SEO allows you to do things like manipulating elements within the DOM (document object model) and running and updating JavaScript code on a web page (we’ll discuss JavaScript updates using Edge later on in more detail).
What are the Benefits of Edge SEO?
There are many benefits to Edge SEO – but here are three key advantages of the technology:
- Ease of Implementation
One of the most obvious benefits of Edge SEO is the ease of implementation. On the Edge, you can implement your SEO recommendations with ease. One of the main reasons behind this is that you are not constrained by the technical limitations of a CMS. The freedom of Edge computing technology allows you to make, for example, on-page SEO changes, without even going near the website’s CMS at all.
- Scale of deployment
As mentioned before, Edge computing is suited for enterprise business applications, and for good reason. Since the Edge exists on a series of distributed data centres, forming a network connection, businesses can deliver and update content much faster. This opens up global opportunities, as deploying your SEO recommendations can be done smoothly and at a large scale.
- Faster dev cycle
Another challenge that SEO professionals often come up against are the limitations of developers – be they in-house or client side. Developers are frequently bogged down with a long list of tasks they need to get through, and somehow each of them seems to be urgent. Thankfully, Edge computing can help with this. With Edge’s capabilities to implement recommendations at speed and do so on a large, global scale, much of the development work should be made easier, thereby allowing for a much faster development cycle.
In fact, many CDNs, such as Cloudflare, have what they refer to as a worker, which includes a front-end interface for non-devs to interact with. This means that SEOs and other professionals not involved in the code of the site can make changes that will better facilitate a user and search engine.
8 Changes You Make on the Edge
The next logical question to ask is what actual SEO tasks can be achieved on the Edge? While the following list is definitely not exhaustive, we’ve highlighted the most salient and foundational tasks to be aware of.
Here are eight SEO tasks that can be achieved using Edge technology. We’ve grouped them into two sections -one for technical SEO implementations and the second for SEO research and testing. The eight SEO tasks can be found below:
- On-page SEO changes
- Managing redirects
- JavaScript updates
- Hreflang implementation
- Website security
- Short term changes
- A/B testing
- Log file collection
Let’s now go on to discuss the first section of SEO tasks, which are primarily for technical SEO.
Edge for Technical SEO Implementation
There are many technical SEO implementations that can be deployed easily using the Edge. With the ability to change almost anything you want, considering you have full access to the Document Object Module, it’s essentially like a pre-render of your website before it is served to the user.
These technical requests can range from managing redirects, to hreflang implementation or manipulating JavaScript code.
1. On-Page SEO Changes
On-page SEO is a fundamental SEO element and is a key pillar in any SEO roadmap. With Edge computing, on-page optimisations can be made on the Edge before it reaches the user. This means that changes can be made dynamically, at a much faster rate and to meet a larger, global demand.
The types of on-page changes that can be made include changing the brand name at the end of a page title and dynamically changing the pricing mentioned in the metadata, based on new pricing decisions. You can also even hold values in a database, stored on the Edge, and then make changes to your on-page copy, by calling on the values, in your Edge database.
This does away with the conventional limitations of making on-page SEO changes. On the one hand, you would typically need to identify a set of pages to optimise, to begin with, then provide your suggestions. If the client has taken it upon themselves to action your recommendations, then this could present its own set of hurdles. Depending on their resources, you could find yourself just waiting around. Or, on the other hand, if you have access to your client’s CMS, or you are working in-house, then you can upload your changes yourself.
However, this presents its own set of problems. Depending on what CMS you are using, like Shopify, Magento or SalesForce Commerce Cloud (SFCC), you will be met with a set of different technical or structural limitations, based on the way your site is built.
Let’s take SFCC as an example. If you have used the platform before, then you will know that, depending on how you have laid out your category or product pages, you can only upload on-page content one at a time. (And let’s not forget the dreadful annoyance of a session time out after 10 minutes of inactivity).
With Edge computing, this limitation can be easily overcome. You can update content dynamically and at a large scale too. In fact, you can even experiment and change a few metadata here and there, depending on your strategy to see if one suggested content will work better than another (more on A/B testing later).
2. Managing Redirects
Managing redirects on your site is also another SEO task that Edge computing can make much easier.
Currently, outside of using the Edge, redirects can be difficult to handle and can quickly become overwhelming. As with optimising on-page content, there are many technical limitations that stem from the CMS. In fact, many businesses and brands have encountered problems when trying to manage redirection on their site due to their CMS. These can include:
- Depending on your CMS, there can be limitations in your ability to implement redirects on the site
- Development roadblocks – if redirects are not something that can be done on the CMS and have to be done manually in the .htaccess file, the changes to this file then depends on the ability of developers and their capacity.
- Another hurdle when implementing redirects on your site, is that it can be considerably time consuming. Again, just like with optimising the on-page content on your site, depending on how your CMS is set up, it can be a case of implementing redirects individually.
However, with Edge computing this can all be avoided and the overall process can be improved upon.
Many CDNs allow for the ability to modify the response code before it reaches the user, thereby serving a redirect in its place.
As discussed earlier, CDNs such as CloudFlare have workers, with front-end interfaces, that can be accessed and used by teams that are not developers. They can manage the redirects themselves, using a CSV file.
3. JavaScript Updates
One of the most exciting capabilities of Edge computing is its ability to write JavaScript code on the Edge and manipulate objects on the page.
This means you can change the way the user interacts with the page on the go, rather than planning to launch extensive code on the page beforehand. This makes it much easier to implement JavaScript on the page, as compared to conventional methods.
And of course, as mentioned previously, since Edge is serverless you don’t have to worry about your JavaScript content being indexed or not, as Google won’t be able to see the difference between the raw HTML and the rendered HTML.
4. Hreflang Implementation
Edge computing can also be used to assist in hreflang implementation, as part of an international SEO strategy (you can also read more about international SEO strategy in more detail in our blog post, on this topic, by our senior SEO strategist Hollie Gibson).
Typically, without using the Edge, you could apply hreflang in three ways.
- First, you could apply the code into the head section of the web page
- Second, you could also apply the code in the XML sitemap
- And third, you could apply the hreflang code in the HTTP header
However, while each of these methods are viable options to implement hreflang code, they might not actually always be applicable. One of the main reasons behind this is that, particularly for many large businesses, while they may have expanded in terms of their operations, their infrastructure, such as their CMS, may not have upgraded in the same way, to match the new international reach of the business.
This is where Edge computing can come in and be beneficial. CDNs such as Cloudflare, can provide another means of implementing hreflang code, in which it changes the direct server response to both search engine user-agents as well as for a user, without actually modifying the underlying code itself.
You can then use any mobile friendly testing tool and check the rendered HTML to see if Google can actually see the hreflang tags, or not, and also use them.
5. Website Security
Edge can also play a significant role in improving the overall security of your website. This is important since site security will play a more central role in Google’s algorithm, as a part of the way Google ranks web pages on their search results page.
We can already see this to a lesser degree now as Google currently warns of malware or if a website has been hacked and is no longer secure. This of course even further serves Google’s intention to provide us with the most authoritative and relevant content to match our searches, but in the most secure and safest way possible.
On the Edge, many CDNs allow you to apply security headers like HSTS, X-Frame options, X-XSS protection, referrer policies and many more.
The application of these security headers on your website will help to protect your site and users from many of the most severe security risks. These security risks can also be detected through passive scanning, which in the future could become a part of Google’s crawling process. So, the fact that we can secure our websites in a way that is in line with Google’s guidelines will benefit not just the search engine but potential users too. It will also make our sites ready for the way Google crawls websites in the future as well.
6. Short Term Changes for Temporary Solutions
It can be the case that you may need to do away with an element on the website, at short notice, but you may not have access to the CMS in order to do so.
If you take, for example, an interactive element that you have on a web page, If this element stops working the way you want it to, then you might want to remove it before it causes users to become frustrated and increase the bounce rate on the page. However, you may not be able to take action on this straight away due to CMS limitations, or without the necessary development expertise at hand at the time that you need it.
With this in mind, the Edge can play a beneficial role in providing a solution. Using Edge computing you could force the web page to return a 503 status code to users and search engines. With this in play, you can then work on removing the dysfunctional element on the page completely and redirect the page in the meantime.
7. A/B Testing
You can also perform A/B testing on the Edge. CDNs such as CloudFlare can access reporting tools like Google Analytics, to track the progress in alterations and other metrics.
On top of this, the process can be done on a large scale, giving you the ability to experiment with, for example, on-page content across various markets. This can be especially beneficial for large brands that operate in various markets.
8. Log File Collection and Analysis
Log file analysis is another typical SEO task that many technical SEOs carry out on their sites. However, while this may be a typical and common SEO task, it might not always be possible to do, for each website you work on.
CMS platforms such as Salesforce Commerce Cloud and Shopify prevent you from collecting log file data at all. That makes carrying out a log file analysis impossible.
However, Edge computing can step in here and provide a solution. Depending on which CDN you use, you may be able to actually obtain logs on the Edge, surpassing any limitations a CMS may present.
Other Edge SEO Abilities
Here are some other SEO activities that can be achieved on the Edge:
- Creating new pages dynamically – this can be done if there is a template already stored in the origin server, by combining it with content stored in a database on the Edge.
- Changing content and styling – This can be done by changing the CSS of a web page or moving content out of tabs.
- Template changes & Testing – You can supply a template for further web page creation. This can be done from the origin server/data centre and then at the Edge, it can be decided which template to apply.
- Creating AMP – With Edge computing you can create accelerated mobile pages that are serverless and entirely in the cloud.
- Implementing schema markup – typically with older CMS platforms the information is already stored on the page, but due to various technical limitations they can’t be applied. Edge is able to add this using a template.
- Adding or modifying headers – this includes HTTP headers, as well as adding robots headers, or even redirects.
Final Thoughts
Edge SEO has an array of benefits to take advantage of and allows for a range of SEO tasks to be achieved. This technology is a game changer to any SEO campaign and to the SEO landscape at large. It has, and continues to change the way SEOs approach their strategies. With local Edge servers placed much closer to the user, around the world, we can take advantage of faster page speed, reduced latency, a global reach and dynamic updates to any site.
As Edge technology continues to grow and advance, the possibilities that can be achieved using this tech are unravelling just as much. Who knows what else we will be able to do on the Edge, in the near future?
I’ll end this blog with a quote from Kevin Indig, which I feel summarises the effectiveness of Edge SEO quite well:
“Edge SEO is an effective way to get stuff done quickly when infrastructure or resource constraints hold you back. Meta-title changes, redirects, or even a/b tests can be shipped and self-served quickly.”
Contact me to talk about how you can begin implementing Edge SEO in your domain.